Understanding MVC Architecture: Model, View, Controller.
 |
| MVC Architecture |
When we talk about organizing code in web development, MVC architecture is used to manage code, maintain code, and for better understanding. Code separation helps manage code effortlessly. Here is a concept of MVC architecture, its a design pattern to manage code separately without any conflicts. In this blog we will understand MVC architecture with example.
What is MVC Architecture?
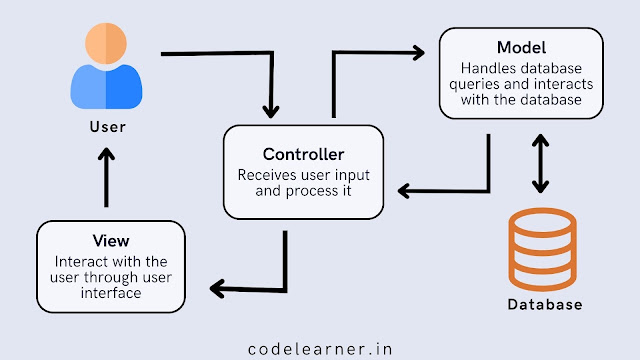
MVC stands for Model, View, and Controller. It is a design pattern that divides code into three components model, view and controller which is interconnected with each other. where model contains business logic and interact with database, view contains user interface to interact with users, and controller acts as intermediary between model and view it receives user input and process it and returns desired response. The separation of model, view, controller helps to organize code, improve maintainability, and promote scalability. Here's an explanation of each component.
Model: Model handles database queries and interacts with data to perform crud (create, read, update, delete) operation. It contains business logic for manipulating data. It receives instructions from controller about what changes to make in the database and after successfully performing the manipulation through the queries it returns the response to controller.
Example: imagine you are building a bookstore app. The model would handle storing and fetching book details like title, author, description, and stock quantity from database.
View: View contains user interface to interact with user, It receives user input or data and sends it to the controller to perform specific task to get the desired output. After controller performs the desired operation it sends the output back to the user through view.
Example: In the same bookstore app, the view would be the page, showing the list of books and title page, including buttons to add books to the cart or check out.
Controller: Controller acts as intermediary between model and view. It receives user input through view and process it and make required changes in the database through model and sends the response back to the view. Controller is responsible for handling the application's behavior.
Example: When user clicks buy now button, the controller will receive that click event and ask the model to update the stock quantity and pass confirmation data back to the view.
Why is MVC Used?
When you build a website or an application, keep things in one place make your code massy, hard to manage, and looks bulky which is difficult to understand. Now the concept of MVC make things clear, it divides code into three component Model, View, and Controller by which you divide your code and put it on these three component Model, View, Controller. Where model handles database, view handles representation of user interface and controller handles event and action performed by user. It helps us to build large scale projects. Laravel, Spring, Django, ASP.NET there are some frameworks which uses MVC Architecture Pattern to build projects.
Let's take an example, If you build a bookstore app and an error occurs when you click the buy now button and the book is not added to the cart, there is no need to check or debug the entire codebase. You just need to check or debug the controller part of you code.
Similarly, if the book title or author is not showing on the screen, you only need to check the view section of you code. This is how the MVC architecture makes debugging easier and more efficient.
How MVC Architecture Works: Step-by-Step
-
The user makes a request to perform some action and sends the request through the View.
-
The Controller takes the user input, processes the request, and performs the required action.
-
The Controller interacts with the Model to add, delete, or update the database.
-
The Model manipulates the database through queries and sends the result back to the Controller.
-
The Controller receives the updated data and passes it to the View.
-
The View displays the final output to the user.
.jpg) |
| MVC Architecture Diagram |
MVC Architecture Example: Bookstore App
Here's a simple and clear example of how MVC architecture works in the real world, Let's take a Bookstore app example using the MVC pattern where you clearly understand how MVC architecture works. In this example we are using Laravel framework for coding to perform crud operation.
Step 1: Create Migration File (Database Table)
In your terminal, run this command:
php artisan make:migration create_books_table
Then update the migration file in database/migrations/2024_02_23_098122_create_books_table.php:
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*/
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('books', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('title');
$table->string('author');
$table->decimal('price', 8, 2);
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*/
public function down(): void
{
Schema::dropIfExists('books');
}
};
Now migrate the table:
php artisan migrate
Step 2: Create Model
In app/Models/Book.php:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Book extends Model
{
protected $fillable = ['title', 'author', 'price'];
}
Step 3: Create Controller
run this command for creating controller file:
php artisan make:controller BookController
In app/Http/Controllers/BookController.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\Book;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class BookController extends Controller
{
// Display list of books
public function index()
{
$books = Book::all();
return view('index', compact('books'));
}
// Show form to create book
public function create()
{
return view('create');
}
// Store new book
public function store(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'title' => 'required',
'author' => 'required',
'price' => 'required|numeric',
]);
Book::create($request->all());
return redirect()->route('books.index')
->with('success', 'Book added successfully!');
}
}
Step 4: Define Routes
Define routes in routes/web.php:
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Http\Controllers\BookController;
Route::get('/books', [BookController::class, 'index'])
->name('books.index');
Route::get('/books/create', [BookController::class, 'create'])
->name('books.create');
Route::post('/books', [BookController::class, 'store'])
->name('books.store');
Step 5: Create Views
Defines in the resources/views folder with the extension of blade.php.
resources/views/books/index.blade.php:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Book List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Books</h1>
<a href="{{ route('books.create') }}">Add Book</a>
@if(session('success'))
<p style="color: green">{{ session('success') }}</p>
@endif
<ul>
@foreach ($books as $book)
<li>{{ $book->title }} by
{{ $book->author }} - ₹{{ $book->price }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</body>
</html>
resources/views/books/create.blade.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Add Book</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Add New Book</h1>
<form action="{{ route('books.store') }}" method="POST">
@csrf
<label>Title:</label>
<input type="text" name="title" required><br><br>
<label>Author:</label>
<input type="text" name="author" required><br><br>
<label>Price:</label>
<input type="text" name="price" required><br><br>
<button type="submit">Add Book</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
This simple Bookstore App example demonstrates the MVC pattern clearly:
- Model - Handles the data (Book.php)
- View - Displays pages (Blade files)
- Controller - Controls logic and flow (BookController)
Conclusion
MVC architecture pattern is widely used design patterns in web development. Whether you are working with Laravel, Django, Ruby on Rails, or ASP.NET, understanding how MVC works in web development that gives you a solid foundation to build better, cleaner, and more maintainable applications, which helps you to build large scale application effortlessly.
MVC architecture is proven approach to writing maintainable, scalable, and clean code. Whether you are building small apps or enterprise-level projects, mastering MVC can make your development process smother and more efficient.
Happy Coding!

.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment